Search for topics or resources
Enter your search below and hit enter or click the search icon.

Smart factory, Industry 4.0, digital transformation, the Internet of things (IoT), and intelligent ERP. We have many new terms, but what do they mean and how do they affect how you manufacture your products?
Let’s start with Industry 4.0. We are in the fourth industrial revolution. The first revolution marked the dawn of factories and the rise of steam-powered machines. The second revolution was all about electricity and saw the birth of the assembly line. The 1960s ushered in the third revolution with automated and computer-assisted manufacturing: MRP, PLCs, automation, and ERP. That brings us to today and Industry 4.0.
Internet, cloud computing, mobile applications, big data and related technologies are the tools of Industry 4.0. Manufacturing uses these to organize and analyze data and then distribute it to a large decision-making group.
One aspect of Industry 4.0 is the Internet of things (IoT)—connecting machines and automating processes on the shop floor. It’s the evolution of the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). How does IoT work? Sensors send information through the internet to a program that then reacts to the data. It’s best explained by examples:
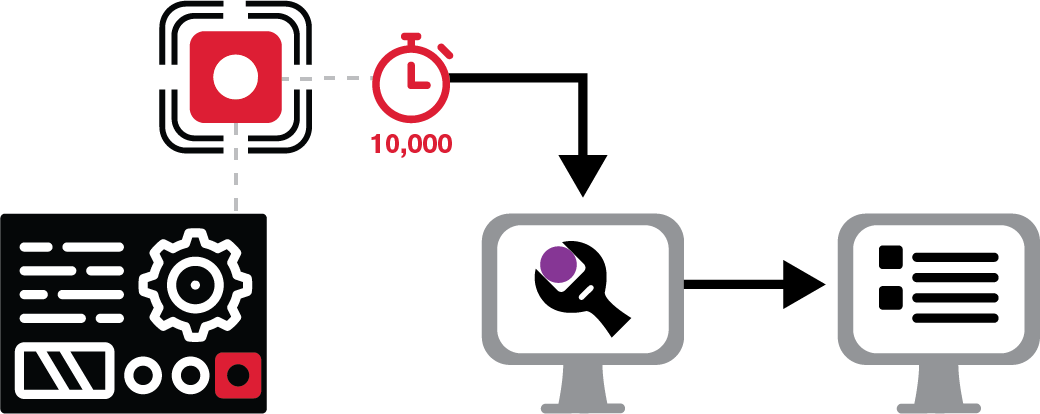 Scenario 1: A sensor installed on a machine on the shop floor records how many hours that machine is in use. When it reaches 10,000 hours, the sensor sends a message to the maintenance program and a preventive maintenance order is automatically created.
Scenario 1: A sensor installed on a machine on the shop floor records how many hours that machine is in use. When it reaches 10,000 hours, the sensor sends a message to the maintenance program and a preventive maintenance order is automatically created.
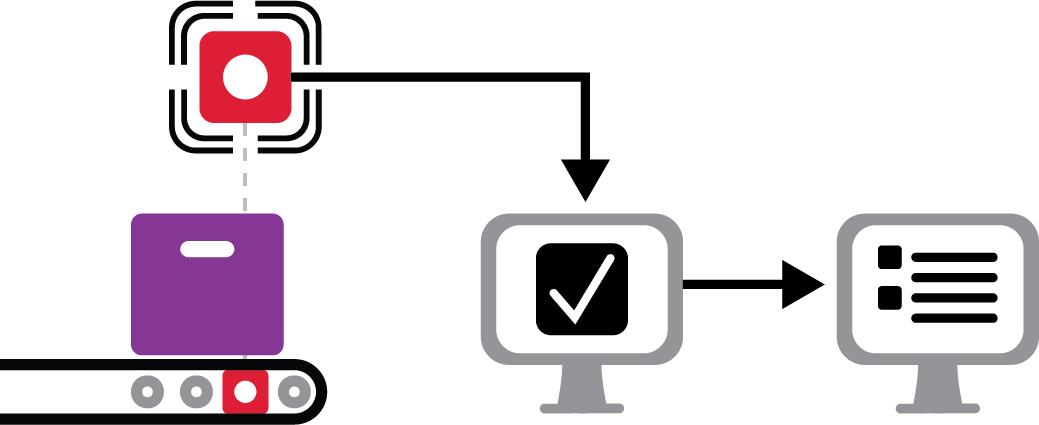 Scenario 2: A sensor is installed at the end of the manufacturing line. When the product moves by the sensor, a transaction is sent to the Work Order Completion program. It then updates the work order and backflushes the material.
Scenario 2: A sensor is installed at the end of the manufacturing line. When the product moves by the sensor, a transaction is sent to the Work Order Completion program. It then updates the work order and backflushes the material.
So how does intelligent ERP fit into Industry 4.0? In the evolution of ERP, intelligent ERP now applies machine learning to provide predictive analytics. It’s the ability to translate data from your ERP system into models and patterns for intelligent decision-making. Armed not only with sales order history, but information about outside trends, weather forecasts, and customer complaints on social media, companies can better determine when and how to manufacture their next product.
This brings us to digital transformation (DX). Think of DX as a cultural mindset. Successful companies use intelligent ERP analytics to better understand the needs of their customer. They embrace rapid proofs of concept, including IoT, to meet those needs. And they redefine roles and processes to complement new technologies. The manufacturing company that is able to make this transformation becomes a smart factory.
Click here to read how ERP Suites consultants helped Stanley Engineered Fastening evolve their business into a smart factory.
Barb Wolter has been providing focused IT solutions for manufacturing customers for over 20 years. As a leader in Oracle’s product development division, she helped drive design, process, testing and quality of innovative products including JD Edwards Orchestrator. Her knowledge and perspective continue to inform digital transformation strategy at ERP Suites with emphasis on smart factory.
Topics: